According to statistics, 15-30% of adults have flat feet. This ratio is probably much higher than you imagined. Indeed, the incidence is relatively high. You might have flat feet without knowing it. I am a person with flat feet.
What is flat foot?
Flat foot, as the name suggests, is when the arch of the foot (known as the medial longitudinal arch) that normally forms a bridge-like curve when standing or stepping on the ground, becomes reduced or disappears in people with flat feet. As a result, the sole of the foot becomes flat, even closely adhering to the ground.
The arch of the foot has three basic functions: support, shock absorption, and load bearing. If the arch disappears, it can cause related functional disorders, such as
Pain in the inner side of the foot, inability to jump on one foot, difficulty in running or jumping, easy fatigue, and other symptoms of flat foot.
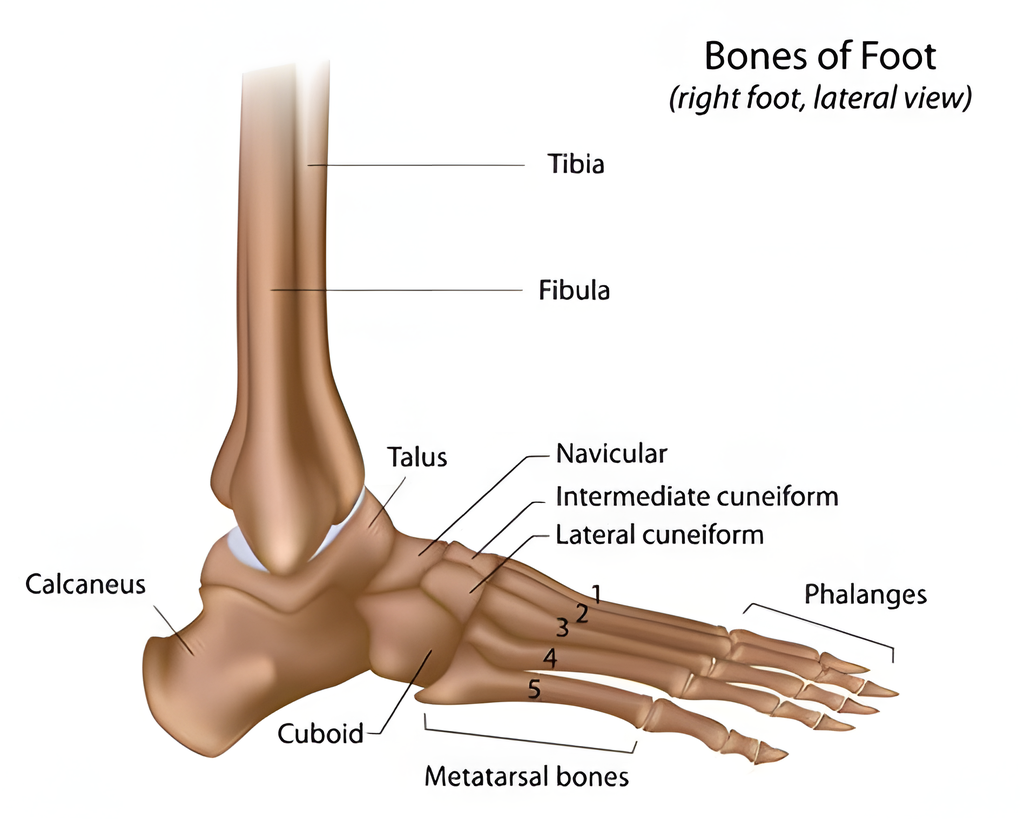
Classification of flat feet
What we refer to as flat feet is different from the condition known as flat foot syndrome. Flat feet can actually be divided into:
- Flexible flat foot, which most of us belong to, accounting for about 90% of cases. The characteristic of this type is that the arch of the foot exists when the foot is not bearing weight, but it disappears when the foot is grounded, which is why it is also known as elastic flat foot, and it rarely causes pain symptoms.
- Rigid flat foot, which accounts for about 10% of cases. It is often related to deformities of the tarsal bones such as the navicular, calcaneus, talus, etc. This means that the bones are connected together, causing the arch of the foot to never appear.
Another type is physiological flat foot. According to statistics, all children under 2 years old have flat feet, and 80% of 3-year-olds do. The arch of a baby and a child’s foot is in the process of gradual development, and the arch will form around the ages of 6 to 9, at the latest by the age of 10. Therefore, it is not unusual to find flat feet in children, and there is no need to worry. It generally does not cause symptoms and is also classified as a type of elastic flat foot.
Flat Foot Syndrome
What needs to be clarified about flat feet is that flat feet are not the same as flat foot syndrome. Flat feet are a type of existence in human foot shape. Only when those with flat feet also suffer from symptoms such as pain when walking can they be diagnosed with flat foot syndrome. Flat foot syndrome often belongs to rigid flat feet or relatively severe flexible flat feet. Patients with flat foot syndrome generally need treatment to correct the deformity.
How to self-check if you have flat feet.
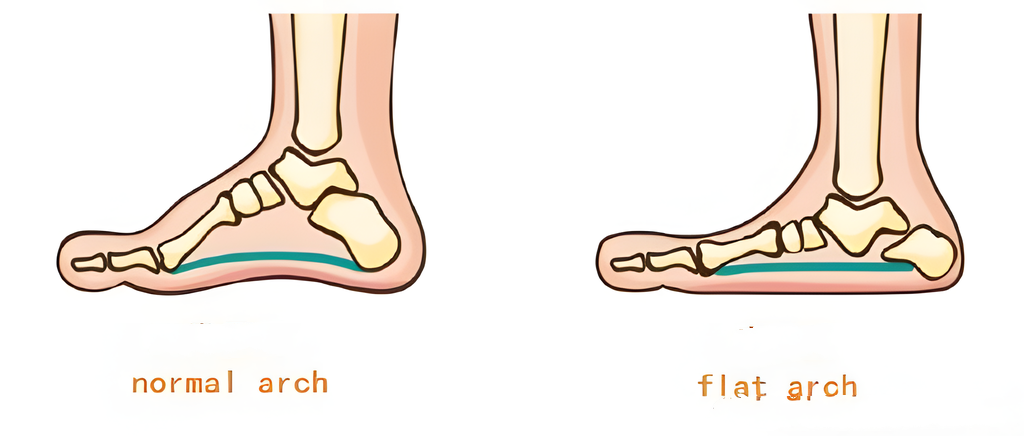
- The simplest method is to lay two sheets of white paper on the ground, slightly wet your feet, then step on each sheet of paper and look at the pressure area of both feet. The wet part of the white paper is the part under pressure. The inside area of the footprint can be referred to the next page’s figure, comparing whether the arch of the foot is relatively high or low. See Figure 3
- Go to the hospital for examination. The doctor may use some more professional judgment methods, such as Feiss Line Method, X-ray examination, etc.
Care and Treatment Precautions for Flat Feet
- Flat feet before school age are mostly physiological, usually without any symptoms, and do not require special treatment.
- Avoid using walkers too early. Some scholars believe that using walkers too early may increase the risk of flat feet, so it is advised to avoid using them too soon.
- Going barefoot is beneficial for the development of the foot arch. A study in India on children’s flat feet found that flat feet are more common among children who wear shoes, less common among those who wear slippers, and least common among barefoot children. As India tends to prefer slippers or going barefoot, its incidence of flat feet is significantly lower than that of the European population. Walking or running barefoot on sandy or sloped grassland is beneficial for foot arch development.
- Obese children are more prone to flat feet, and weight plays an important role in the occurrence of flat feet in children. Many surveys indicate a correlation between the posture of a child’s foot and their weight. Studies show that starting from the age of 8, if overweight or obesity persists into adulthood, structural changes in the foot can cause injurious changes to the function of the medial longitudinal arch (key to flat feet). Therefore, it is suggested to avoid obesity.
- You can perform some foot exercises regularly, such as picking up beads, grabbing towels, small paper balls, or pencils with your toes, which can train the strength and endurance of a child’s foot muscles. Walking on heels (like a penguin) can train a child’s lower limb strength and promote the formation of the foot arch.
- Choose the right size shoes, not soft shoes: shoes too small will lead to toe compression deformation, too large when the foot to excessive force to grasp the sole, toes are prone to deformation.
- If a child experiences foot pain, they need to be examined by an orthopedic doctor. If they indeed have a severe case of flatfoot, orthotic devices or insoles may be necessary to support the arch of the foot as a form of treatment.

0